Types of Bitumen Grades
What is bitumen?
Bitumen is a black, pasty substance that is used in moisture insulation and asphalt construction. There are different types of bitumen grades and it has been used in making construction and decorative items, artificial prostheses, ship waterproofing and even embalming. Bitumen is a petroleum derivative.
Bitumen naturally occurs under the earth’s crust in the form of springs, lakes and surface mines in solid and liquid form. In fact, it was natural bitumen that was used in the past by human ancestors and was used in road construction in the late 19th century, and finally with the discovery of oil and its refining and the creation of bitumen residue, the way for the wide use of bitumen in the road Sazi opened.
Asphalt surfaces made with the help of bitumen today provide very smooth and safe roads for light and heavy vehicles and quality runways for landing and takeoff of airplanes and even very good rail infrastructures for trains.
Building waterproofing and industrial applications, such as protective coatings for oil and gas transmission lines and power transmission lines, all indicate the ability to cover and waterproof bitumen.
Ingredients of Bitumen:
The different compounds of bitumen are not well known so far, but the majority of these compounds, which are separated from bitumen by different solvents, are asphaltene resin materials and heavy oils, which are sometimes accompanied by a small amount of minerals and are placed in an oily colloidal environment adjacent to each other.
The property of flexibility and adhesion of bitumen is related to resin, on the other hand, the more asphaltene is, the harder the bitumen is, but with the increase of bitumen oil, it becomes softer. By heating bitumen, oily substances turn into resin, and also resins turn into asphaltene, and in too much heat, bitumen turns into coal and water vapor.
- Asphaltene
Asphaltene is a brittle solid substance that is insoluble in normal heptane and has a black to brown color. In addition to carbon and hydrogen, it has some nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. Asphaltene is usually considered a very polar compound and contains complex aromatic substances with a very high molecular weight.
- Maltans
Maltenes are soluble in light solvents such as normal heptane. The maltenes in bitumen are a mixture of resins and oils, and the molecular weight of the maltene components is between 250 and 1250 g/mol.
- Resins
Resins are soluble in normal heptane. Most of these compounds, such as asphaltene, consist of carbon and hydrogen and also contain a small amount of oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen.This material is solid and semi-solid in dark brown color and is very polar. The special feature of resins is that they are very sticky.
Resins are anti-coagulants for asphaltene, and the ratio of resin to asphaltene can be adjusted to the extent that it gives the bitumen a sol or gel state.
- Aromatics
Aromatics are cyclic compounds with the lowest molecular weight and contain aromatic or naphthenic side chains and are considered very suitable anti-coagulants for asphaltene. This component constitutes between 40 and 60% of the total bitumen and is a dark brown viscous liquid whose average molecular weight fluctuates between 300 and 2000.
Aromatics contain non-polar carbon chains in which saturated rings are preferred and have great solubility for other heavy hydrocarbons.
Saturated Compounds:
Saturated compounds consist of straight and branched chain aliphatic hydrocarbons along with alkyl naphthenes and some alkyl aromatics. These compounds are often in the form of viscous, non-polar and colorless oils.
Their average molecular weight is the same as aromatic and their constituents include saturated waxy and non-waxy materials. This component constitutes 5 to 20 percent of bitumen.
In general, asphaltenes form the structural skeleton of bitumen, and resins are effective in the amount of adhesion and plasticity of bitumen, and oils affect the psychological problem of bitumen. Basically, the physical properties of bitumen are a function of the chemical structure, quantity and quality of hydrocarbons.
Applications of bitumen:
Bitumen is usually used in two areas: road construction and insulation. About 90% of the produced bitumen is used in the field of road construction, and insulation costs account for only 10% of the bitumen consumption, which consists of:
Covering floors, roofs, underground pipes, protecting metals, as well as sealing tanks, canals, bridges, and stabilizing flowing sand, painting, etc.
Petroleum Asphalts
They are the type of bitumen whose origin is crude oil. These bitumens are solid and semi-solid bitumens that are obtained directly from the distillation of crude oil or by other additional operations such as blowing air, and they have more applications and higher consumption than other types of bitumen.
Blown bitumens:
Petroleum bitumens are prepared by two methods of direct extraction (Straight Run) and air blowing (Air Blowing). The aeration method is used when the bitumen raw material (feed) does not have the expected characteristics. In this case, by blowing air into the raw material (feed) at a temperature between 190-200°C, a product with modified properties is produced.
This process is sometimes called Asphalt Oxidation and its product is called Oxidized Asphalt, but the terms Air Blowing and Air Blowing Asphalt are more appropriate, because in this process, polymerization ) and dehydrogenation (dehydrogenation) is done and oxygen will not enter in the aeration product except in very small amounts.
In the industry, it is done in two continuous ways (Continues Process) and discontinuous (Batch Process).
Production bitumens are classified and named according to the amount of aeration based on tests in accordance with international standards.
The most reliable global standards are Viscosity Grade, Penetration Grade and Performance Grade.
The raw material for the production of petroleum bitumen is vacuum bottom (VB) which is used to produce 60/70, 85/100 and other bitumen grades.
1- Batch Process
In the discontinuous process, the aeration tower is filled with a certain volume of feed and after blowing air with predetermined conditions (reaction temperature, time, amount of feed) and the product reaches the desired specifications, the tower is emptied and the product is stored in the desired tanks. enters
The main components of the continuous aeration unit are:
:: Pre-heater oven
:: Blower or Compressor
:: Oxidizer Tower
:: A system for collecting and burning vapors
2- Continuous Process
In the continuous process, the feed with a definite and controllable flow rate and predetermined temperature continuously enters the aeration tower and after performing the aeration operation under constant operating conditions, it continuously leaves the aeration tower. This bitumen preparation method, which is used in refineries, is considered for the following advantages:
:: Reduction of polluting vapors created
:: Reducing the cost of equipment and maintenance
:: Increasing efficiency and amount of production per unit of time
:: Reducing the thermal load of feed preheaters
:: Ease of process control and operation due to the continuous nature of the process
:: Reducing the air consumption and shortening the aeration time due to the optimal use of blown air
The important use of bitumen is due to the presence of two important properties of this substance;
* Impermeable to water
* Stickiness
Bitumen is usually obtained from the distillation of crude oil. Such bitumen is called petroleum bitumen or distillation bitumen. Petroleum bitumen is the product of two stages of crude oil distillation in the distillation tower.
In the first stage of distillation, light substances such as gasoline and propane are separated from crude oil. This process is done at a pressure close to one atmosphere (unit).
In the second stage, heavy compounds such as diesel and kerosene are removed. This process takes place in a pressure close to vacuum. Finally, a mixture of very fine solid particles called asphaltene remains, immersed in a grease-like fluid called maltene.
But some types of bitumen are obtained in nature as a result of the gradual transformation of crude oil and the evaporation of its volatile substances over many years. Such bitumen is called natural bitumen and it is more durable than petroleum bitumen. Such bitumen may exist pure in nature (lake bitumen) such as Behbehan Bitumen Lake in Iran and Trinidad Bitumen Lake in America, or be extracted from mines.
How is bitumen produced:
1- Direct execution
2- Blowing air, which is done as an intermittent or continuous process.
Types of bitumen grades and bitumen resources and applications:
Bitumen materials are more diverse than oil, because bitumen has other sources besides oil. Bitumens are divided into the following three categories depending on their origin:
1- Natural bitumen
2- Petroleum bitumen
3- Tar tars
Until the end of the 19th century, bitumen used in road construction and street construction was mineral bitumen, stone bitumen, bituminous mastic and stone powder, which is considered as mineral or natural bitumen.
In the early 20th century, petroleum bitumen obtained from crude oil refining came to the market and replaced mineral and natural bitumen in asphalt pavements and other industrial uses.
Direct extraction of bitumen from crude oil:
Distillation is a fundamental process in refining crude oil. The first stage of distillation is done under atmospheric pressure and usually involves heating the crude oil to a temperature of about 650 to 800 degrees Fahrenheit and then injecting it into a separation column.
In this way, the lighter cuts as a product of the top of the tower and the bituminous residue are called atmospheric residue. This is the first step in the entire purification process. Many crude oils contain high percentages of high-boiling fractions that cannot be distilled in an atmospheric still. To separate these cuts and prepare bitumen with desired characteristics, a secondary separation tower that works in vacuum conditions is used.
The remainder of this process is called direct extraction bitumen. Asphalt production process by vacuum distillation method has very little effect on other bitumen properties except permeability. The origin of the used crude oil also has a significant effect on the physical properties of extracted bitumen.
What is the application of bitumen vacuum batum?
Crude oil is refined in a refinery to obtain petroleum derivatives. In the refinery, this oil is transferred to the distillation towers and divided into its components. The reason for the separation of crude oil components from each other is the difference in boiling point in different parts of the tower.
The lowest layer that remains as a result of crude oil distillation under vacuum conditions in tar towers is called the vacuum bottom. In the past, this vacuum bottom was known as crude oil sludge and was thrown away.
With the passage of time and the advancement of technology, engineers were able to turn the vacuum baton into a usable material by performing certain processes. In fact, the material obtained from the vacuum baton is bitumen and fuel oil. 70% of fuel oil raw material is vacuum baton (VB).
What are the characteristics of bitumen vacuum batum?
Vacuum Batum looks and smells like bitumen and is produced in a dark color. This material is chemically stable but flammable. Batum vacuum consists of hydrocarbons whose number of atoms is more than 35.
The temperature of the vacuum floor inside the distillation towers is 240 to 320 degrees Celsius, the oxidation process starts when the air passes through the vacuum floor at the said temperature. The result of blowing air into the baton vacuum is improving its properties and converting Meltan molecules into heavier molecules, namely asphaltene. The created molecular transformation causes the formation of bitumen with a low degree of penetration and an increase in its smoothness.
Characteristics of the vacuum floor
Among other characteristics of the vacuum floor obtained in tar towers, the following can be mentioned:
Density at ambient temperature (25°C): 1010-1020 kg/m3
Penetration degree: 22-33 mm
Viscosity at 100 degrees Celsius: 450-900 centigrade
Now, after getting acquainted with the specifications of the vacuum bottom, it is time to ask: What is the application of vacuum batum bitumen? Vacuum baton is used in the production of fuel oil and bitumen, and in other words, it is the raw material for the production of these two products.
Modified bitumens
In order to achieve suitable mechanical properties, bitumen modifying polymer is used to change their natural rheological properties. The widespread use of plastics and rubbers in various sectors such as industry, agriculture and even in daily life leads to the creation of a lot of polymer waste and important environmental problems.
In order to solve this problem, new ways were investigated. Therefore, from the economic and environmental point of view, it is beneficial to use waste polymers as a bitumen modifying polymer, so that the modified bitumen properties of waste polymers are similar to the properties of modified bitumen with first-hand polymers.
In general, we consider two categories of waste polymers:
1- Thermoplastic waste polymers
2- thermosetting waste polymers
Adding such polymers to bitumen leads to improvement of thermomechanical resistance. Polypropylene and EVA increase the elasticity and cohesiveness of bitumen.
In relation to waste polymers (rubber powder obtained from waste tires), CTR Thermosting must be said to be the best example of this model. Westnamer polymer (polyoctanemer) is a polymer additive only in combination with rubber powder. Rubber powder with polymer. This polymer facilitates asphalt modification with rubber powder.
This Westnamer polymer is a suitable replacement for other bitumen and asphalt modifiers such as SBS, which can be added to bitumen or asphalt in a dry method.
Bitumen Emulsion:
Qirabah (emulsified bitumen) is obtained by mixing bitumen and water with an emulsifying agent. The amount of emulsifier is very low and is around 0.3 to 0.5% of the weight of bitumen. The amount of water used in this type of bitumen is around 30% to 50% of the weight of bitumen.
The emulsifier is usually an alkaline salt of organic acids or an ammonium salt that charges the bitumen particles.
In this way, the bitumen particles repel each other due to the induced charge and float in the water as spheres with a diameter of one hundredth to one thousandth of a millimeter. Using this type of bitumen reduces environmental pollution and because oil or flammable solvents are used If not, the risk of ignition during bitumen transportation is reduced.
Emulsion bitumen can be used instead of MC bitumen after the completion of the road infrastructure and before the start of asphalt spreading, and it is also used to produce concrete asphalt or insulation.
Another use of this product in agricultural land is to prevent water evaporation and reduce soil moisture.
Soluble Bitumens:
Soluble bitumen is a mixture of bitumen and a suitable solvent (for example, kerosene or gasoline). The type and quality of soluble bitumen depends on the quality of the original pure bitumen, the type of solvent and the amount of solvent. This bitumen is liquid at ambient temperature or turns into liquid with a little heat.
Soluble bitumen is used in all kinds of asphalt coverings. The speed of setting or hardening of this type of bitumen depends on the type of solution. The lack of access to bitumen heating devices, the decomposition of bitumen at high temperatures, the cooling of bitumen during work, the impossibility of its penetration into porous minerals, the need for workers’ safety, fire and time-consuming causes that in some cases, bitumen solution should be used.
Soluble bitumen is used in road construction for surface coatings, infiltration, industrial cold asphalt or mix on site.
Soluble bitumens are divided into the following 3 groups according to the setting speed and type of solvent:
– Qirtandgir (RC):
Due to the high evaporation rate of gasoline, bitumen dissolved in gasoline hardens faster. This bitumen is called fast-acting bitumen.
– Bitumen retarder (MC):
The bitumen dissolved in kerosene is called retarder bitumen, the rate of evaporation of oil is slower and longer than gasoline.
– Girdirgir (SC):
Bitumen that dissolves in gas oil or fuel oil is called slow-setting bitumen.
Petroleum bitumens are produced by three processes: direct extraction, straight run, air blowing, and blending.
Specifications of Bbitumen Grades:
1- degree of penetration:
Penetration degree test is used to determine bitumen hardness. In this test, a standard needle penetrates into bitumen at a temperature of 25 degrees for 5 seconds under the effect of a load of 100 grams. The amount of penetration in tenths of millimeters is called the degree of penetration. The lower the degree of penetration, the harder the bitumen.
2- Viscosity:
The higher the flow rate of bitumen, the more solid properties it exhibits. It is clear that the mental retardation is less at higher temperatures. This characteristic of bitumen is measured with C-bolt Fiorel device or by kinematic method.
3- Degree of Ignition:
The degree of ignition is the temperature at which if the bitumen reaches that temperature, the gases emitted from it will ignite as the flame approaches and a flame will appear on its surface. The maximum temperature that bitumen can be heated in the workshop is limited to the degree of ignition.
4- Weight Loss:
The weight loss of bitumen at high temperature is due to the evaporation of part of its oils and petroleum compounds. This feature is also one of the important properties of bitumen. The weight loss of bitumen is measured in the oven at a temperature of 163 degrees Celsius and in a period of 5 hours (approximate asphalt baking conditions).
5- Malleability or Malleability:
If we pull a sample of bitumen with a cross-sectional area of 1 square centimeter at a speed of 5 cm/min, the amount of increase in the length of the sample before tearing is called the enemic property of bitumen.
6- Degree of Purity:
We know that the solvent of bitumen is carbon tetrachloride and carbon sulfur. Therefore, if we dissolve a sample of bitumen in any of these substances, its impurities will remain, and from there we can determine the degree of purity of the bitumen. The degree of purity is: (bitumen sample weight) ÷ [(impurity weight) – (bitumen weight)]
7- Degree of Softness:
Softness degree is the temperature at which the bitumen turns from solid to liquid when bitumen reaches that temperature. The higher the degree of bitumen softness, the less sensitive it is to temperature changes. The degree of softness of ordinary bitumen is about 60 to 70.
What is the use of bitumen in road construction?
Bitumen is used in a large amount, about 85%, in the road construction industry. Another use of bitumen can be mentioned as a waterproofing. In general, it is possible to use bitumen in more than 7 different fields, and in these 7 fields, there are more than 130 types of applications.
What is the reason for using bitumen in the construction of buildings? Due to its adhesion and sealing properties, bitumen is widely used in all aspects of civil engineering and construction. Penetration bitumen and emulsion are used to build railway lines, and modified polymer bitumen is also used in the railway industry to reduce noise and vibration.
Due to the resistant structure of PMB, the coating of airport runways is modified from polymer. Bitumen is used in wide and important dimensions for the marine construction industry such as: canal lining, underground tunnels, protection of river banks, construction of dams and docks in the sea.
You may be interested to know that bitumen is also used in roofing felt, printing ink, packaging paper, electrical cable insulation, junction box, etc.
Buying Imported Bitumen
Iran is the largest bitumen producer in the Middle East. Iran exports more than 4 million tons of bitumen annually in various packages with different transportation methods. The number of bitumen export destinations reaches more than 30 countries. The production capacity of bitumen in Iran is over 6 million tons, of which about 2 million tons are used inside Iran.
* You can use the advice and experience of Atra Atlas Trading Company to import all types of Iranian bitumen grades.
How to import bitumen from Iran:
The import of Iranian bitumen is carried out by sea and land in bulk packages, barrels and bags. Bulk bitumen is exported by land routes by tankers and by ships by sea route.
– Barrels in 150, 185 and 22 kg sizes.
– Jumbo Bag: Jumbo bag is a type of eco-friendly and cost-effective packaging that is available in various sizes.
Bitumen has many grades, but the most types of bitumen grades used in Brazil are:
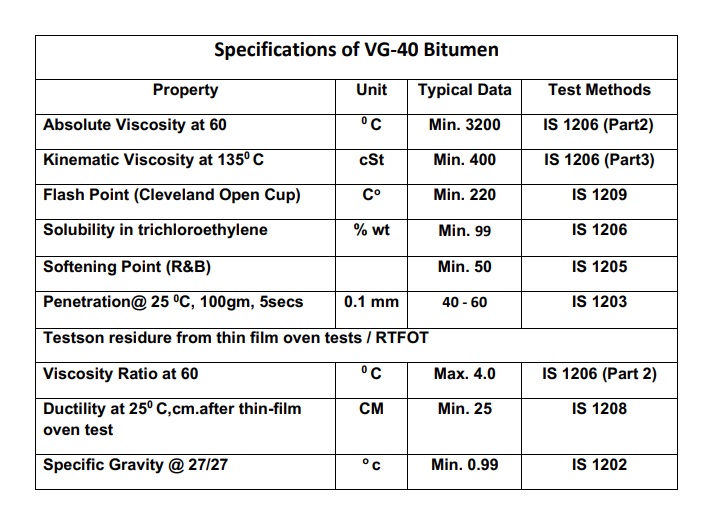
*** VG30
VG GRADE bitumen is called a grade of refinery bitumen obtained from the vacuum aeration of the distillation tower and divided according to their viscosity. The most common use of this type of bitumen is in road construction, insulation, building construction and liquid bitumen production. In terms of place of use, VG30 bitumen is more suitable for temperate climates.
In the classification based on the viscosity of bitumens according to the value of absolute viscosity at 60°C or kinematic viscosity at 135°C, the classification and direction of each of them have been determined by specific technical standards. Absolute viscosity is expressed in poise and kinematic viscosity is expressed in centi-Stokes. Classification and characteristics of pure bitumen are reported in AASHTO-M226 and ASTM-D3381 standards.
The higher the temperature, the harder the bitumen is. In the viscosity grade, the viscosity test is measured at 60 and 135, which is the temperature of the road surface in summer and the temperature of mixing asphalt, respectively.
The degree of penetration at a temperature of 25 degrees, which is the average annual temperature of the asphalt coating, is also specified in the specifications of this bitumen standard.
Distillation is a fundamental process in refining crude oil. The first stage of distillation is done under atmospheric pressure and usually involves heating the crude oil to a temperature of about 650 to 800 degrees Fahrenheit and then injecting it into a separation column.
In this way, the lighter cuts as a product of the top of the tower and the bituminous residue are called atmospheric residue. This is the first step in the entire purification process. Many crude oils contain high percentages of high-boiling fractions that cannot be distilled in an atmospheric still. To separate these cuts and prepare bitumen with desired characteristics, a secondary separation tower that works in vacuum conditions is used.
The remainder of this process is called direct extraction bitumen. Asphalt production process by vacuum distillation method has very little effect on other bitumen properties except permeability. The origin of the used crude oil also has a significant effect on the physical properties of extracted bitumen.
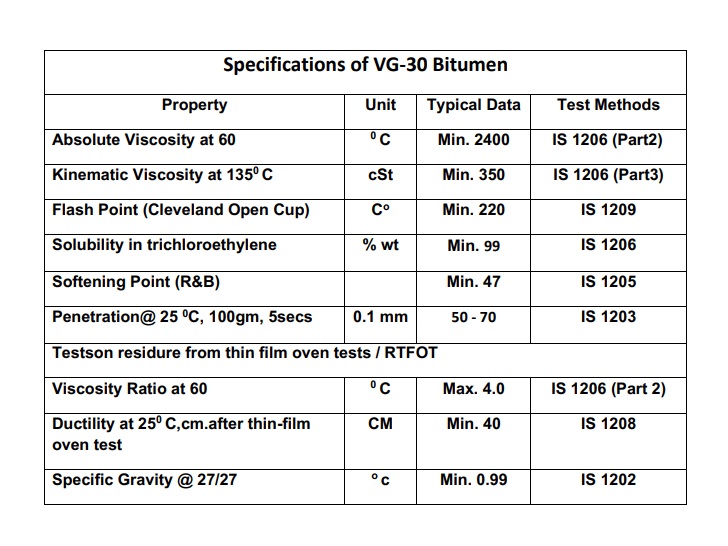
*** VG40
VG40 bitumen is one of the types of bitumen classified according to viscosity.
Viscosity is a fundamental property of bitumen that determines how materials behave at a certain temperature or a temperature range. In terms of application, VG40 bitumen is more suitable for warmer climates.
In the classification based on the viscosity of bitumens according to the value of absolute viscosity at 60°C or kinematic viscosity at 135°C, the classification and direction of each of them have been determined by specific technical standards.
*** Grade 50-70
It is a bitumen that is obtained by carrying out the oxidation process on vacuum batum (the raw material of bitumen production which is obtained from the bottom of the distillation tower in the vacuum of oil refineries) in the bitumen units in such a way that the degree of permeability (a type of test to determine The hardness of bitumen should be between 50 and 70.
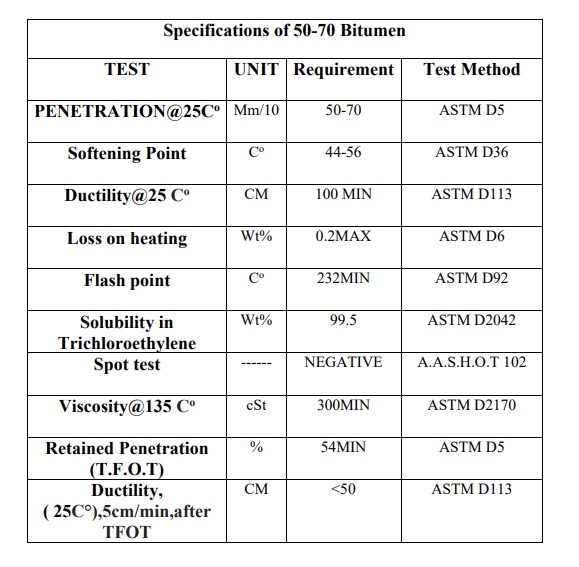
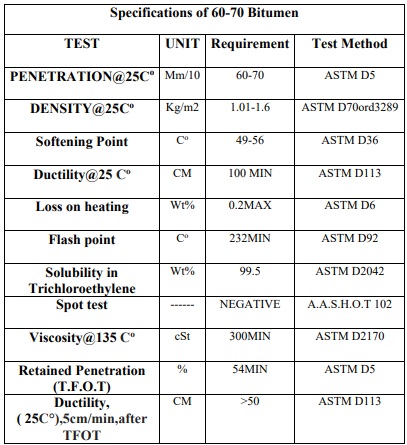
*** Grade 60-70
Bitumen 60/70 is a type of penetrating bitumen that is produced using vacuum batum oxidation. Permeable bitumen or road grade is used to produce asphalt.
Penetrating bitumens are obtained by aeration process on the residue of the distillation tower, which is known as vacuum baton. Because the degree of permeability of this type of bitumen is between 60 and 70, they are known as 60/70 bitumen. Bitumen 60/70 is more suitable for temperate climates.
The state of bitumen 70/60 depends on its temperature.
The temperature and hardness of bitumen depends on the type of crude oil and its refining method. The degree of permeability of 70/60 bitumen is between 6 and 7 mm and it is suitable as a heavy bitumen for building and repairing roads.
60/70 bitumen is used for asphalt production and it is mainly used for surface coating in hot asphalt production.
Bitumen 60/70 is the most widely used among all types of bitumen and is considered a raw material for other bitumen products.
Permeable bitumens with road grade grading, which are mostly used for asphalt production and road construction. This bitumen is purchased from refineries in the form of a seal and is packaged with the highest quality and in accordance with international standards. Bitumen 60/70 is usually used in temperate climate regions.
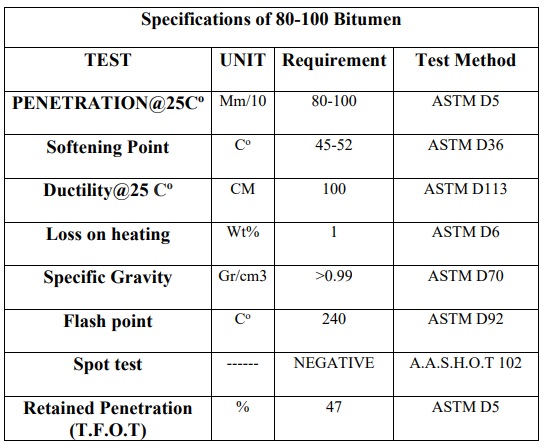
*** Grade 80-100
Bitumen is completely soluble in carbon disulfide (CS2) and has the ability to stick and be waterproof. It is mainly composed of hydrocarbons and is usually made up of about 80% carbon and 15% hydrogen, with the balance being oxygen, nitrogen and other trace elements.
Penetration-grade bitumen is commonly used in road surfaces and minor industrial applications. Permeability determines the hardness of bitumen by measuring the depth that a standard needle-load penetrates vertically in 5 seconds, in an example of Bitumen stored at 25 degrees Celsius
Viscosity grade bitumen asphalt can be used on original asphalt that is grades AC (Asphalt Cement) or old residual grade AR (Aged Residual).
It is used in hot climates because of its high viscosity.